应该使用 GET/POST 获取返回 200 的状态码的 API
似乎所有人都这么做
经常做爬虫的时候总会观察到这么一个现象,很多网站的API都会返回 200 的状态码,即使是请求失败了,也会返回 200 的状态码,然后在返回的数据中会有一个 code 字段,用来表示请求是否成功,比如:
{
"code": "not_found_user",
"data": null,
"message": "用户不存在",
"success": false,
"statusCode": 404
}
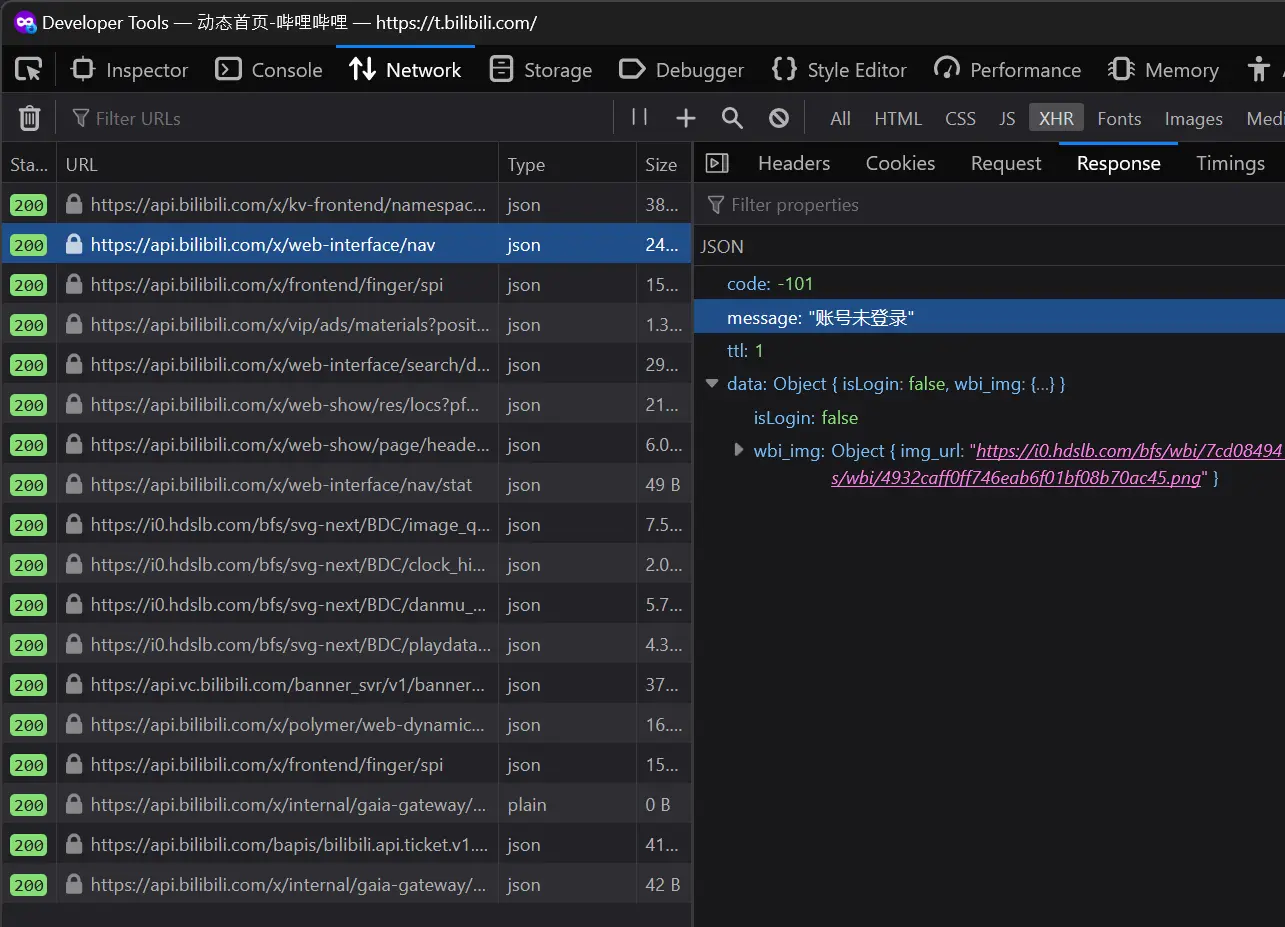
正好也看到知乎的一个讨论:为什么那么多公司做前后端分离项目后端响应的 HTTP 状态一律 200?

感觉确实很对,从运维的角度来看,这样做确实会方便很多。例如 vercel 的 log 对于大于 400 的状态码都会标黄或是标红,但很多时候都是只业务层面的错误,而不是系统层面的错误,这样的话就会造成很多误解,而且也不方便排查问题
而对于开发来讲,有些 fetch 客户端对于大于 400 的状态码都会抛出异常,这样的话就需要在每个请求的地方都去捕获异常……
再就是,面对复杂的业务逻辑,HTTP 状态码的表达能力实在是不足。虽然也能塞业务 code 到 body 里,但还是有些麻烦hhhh
当然,还有个月经问题是,GET/POST 比 RESTful API 会舒服、直观很多,把操作方法放在 url 而不是 Method
所以再见了,RESTful API😹
实现
先说后端,我们可以继承自 Error 的类 MyError,然后设定一系列的业务错误码,然后在业务层面抛出 MyError 的实例,然后在中间件中捕获这个错误,以 200 的状态码返回
这里还涉及到了一个思想,就是不再使用频繁地使用 try-catch 来捕获异常,而是只用 throw 掉它,再在全局的地方去捕获它,这样的话就可以减少很多重复的代码
Nuxt Server
以 Nuxt.js/Nitro 为例,它支持手动配置全局的异常处理函数:errorHandler。需要现在 nuxt.config.ts 中添加:
export default defineNuxtConfig({
nitro: {
errorHandler: '~/error/nitroErrorHandler.ts',
},
})
然后捕获函数:
export default <NitroErrorHandler> async function (error: MyError, event) {
const code = (error.cause as any)?.code || error.code
const err = newError(code, undefined, error) // 根据 code 生成新的错误
const { message, ...rest } = err
if (err.statusCode >= 500)
consola.error({ ...error })
const res = event.node.res
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'application/json')
res.statusCode = 200
res.end(JSON.stringify({ message, ...rest }))
}
其中,对于错误码的定义,可以这么写
export const Errors = [
{
code: 'unknown error',
message: 'Server error',
statusCode: 500,
data: {},
},
] as const // as const 在类型系统中特别好用
// the handled error codes
export const errorCode = Errors.map(e => e.code)[0]
export type ErrorCode = typeof errorCode
得益于 as const,这里的 ErrorCode 的类型全是字面量字符串,提供了很好的类型补全。这样就不用使用枚举来实现了,只需要输入特定的字符串即可完成类型检查
对于返回的类型,可以这么写
export type ErrorReturn = Omit<ApiReturn, 'code'> & {
code: ErrorCode
}
/**
* the api return type
*/
export interface ApiReturn<T = any> {
code: ErrorCode | 'ok'
statusCode: number
message: string
data?: T
}
Nest.js
Nest.js 是支持自定义异常处理的,实现 ExceptionFilter 即可
// /common/filters/any-exception.filter.ts
@Catch()
export class AnyExceptionFilter implements ExceptionFilter {
catch(exception: any, host: ArgumentsHost) {
const ctx = host.switchToHttp()
const response = ctx.getResponse<Response>()
const code = exception.code || 'unknown error'
const error = newError(code, null, exception)
response.status(200).json(error)
}
}
然后在全局模块中添加:
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common'
import { APP_FILTER } from '@nestjs/core/constants'
import { AnyExceptionFilter } from './common/filters/any-exception.filter'
@Module({
providers: [
{
provide: APP_FILTER,
useClass: AnyExceptionFilter,
},
],
// ...
})
export class AppModule {}
Spring Boot
SB 可以捕获在 Controller 中抛出的异常,然后在全局的地方去处理它,这里需要用到 @ControllerAdvice 注解,然后在类中添加 @ExceptionHandler 注解
@ControllerAdvice
class GlobalExceptionHandler :
BasicErrorController(DefaultErrorAttributes(), ErrorProperties()) {
@ExceptionHandler(Exception::class)
fun handleException(ex: Exception): ResponseEntity<ApiReturn<Nothing?>> {
if (ex !is MyError) {
ex.printStackTrace()
return response(ErrorCode.UNKNOWN_ERROR, 500, ex.toString(), null)
}
return response(ex.code, ex.statusCode, ex.message, null)
}
}
但是,对于在 controller 层之前抛出的错误,如 Filter 等,就需要在 Filter 中手动捕获,然后重定向到一个特定的 error url,然后在这个 url 中再抛出错误,这样才能被 @ControllerAdvice 捕获到
其中,包装的统一 api response 的函数:
data class ApiReturn<T>(
val code: ErrorCode = ErrorCode.OK,
val statusCode: Int = 200,
val message: String = "ok",
val data: T? = null
)
fun <T> response(
code: ErrorCode = ErrorCode.OK,
statusCode: Int = 200,
message: String = "ok",
data: T
) = ResponseEntity.ok(
ApiReturn(code, statusCode, message, data)
)
而一系列的错误码可以通过一个枚举类来定义
enum class ErrorCode {
OK,
UNKNOWN_ERROR,
// ...
}
data class MyError(
val code: ErrorCode = ErrorCode.UNKNOWN_ERROR,
val statusCode: Int = 500,
override val message: String = "Internal Server Error",
) : Exception()
val Errors = listOf(
MyError(ErrorCode.NOT_FOUND_USER, 404, "User not found"),
// ...
)
fun newError(code: ErrorCode) = Errors.firstOrNull { it.code == code } ?: MyError()
